ANTENNA DIVERSITY
One way to achieve diversity isusing a two- channelreceiverthat is free from fading . The possibility of both is affected by fading in the same time is small. This method requires 2 Rx antennas at the Base Station to receive the same signal, it is not affected olehkarena differences caused by fading.
By selecting the best of the two signals, due to fading can be reduced. There are two ways to do this, namely:
Space Diversity: The distance between the antenna must be such relationships in the two-antenna signal, which is low. Relationships are the equations that describe the statistical limits of the signal. In practice, the distance should be a few meters. At 900 MHz is possible strengthening of 3 dB, used a distance of 5 to 6 meters between the two antenna .. At 1800 MHz the distance would be minimized because a smaller wavelength.
Polarization Diversity: Antenna Dual Polarization is: an antenna device with 2 rows with the same physical unit. Both lines can be arranged and directed in various ways during the second plan of polarization have the same performance by strengthening and examples of radiation. Two forms are commonly used together, namely: Vertical and Horizontal rows and rows in the slope of 45 °.
Formatting BURST
Information superimposed on one time slot in TDMA frame by Air Interface commonly called Burst (split). TRU (contained in the RBS) and MS perform the function of putting information into the form of actual burst. There are five different types of burst, namely:
NORMAL BURST
Used to carry information on the Traffic Channels and Control Channels; BCCH, PCH, AGCH, SDCCH, SACCH and FACCH.
Normal burst contains 57 bits of data packets encrypted or voice, 2 flag bits, 26-bit Training Sequence, and two packages of 3 bits, called tail bits. Flag bits (Stealling flags) indicate the FACCH signal is in the process. Training sequences are known as examples of bits used by the equalizer to make the channel model. Tail bits are always 0,0,0 and used to help the equalizer indicate start and stop points. A ts is room to 156.25 bits, but the burst only contains 148 bits. Time 8.25 empty and called the Guard Period, which is used to protect the burst of overlapping and others.
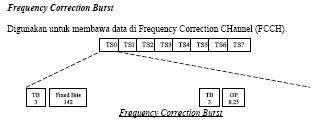
Frequency Correction Burst
Used to carry data in the Frequency Correction Channel (FCCH).
Synchronization Burst |
Access Burst
Used to carry data in Random Access Channel (Rach). It has a Guard Period longer to justify the fact that MS does not know the timing advance value for transmission on the first access. MS can be far from BTS that indicates the initial burst would arrive late.
Dummy Burst
Not carry information, and sent from the BTS on ts who are not carrying traffic, providing the charging carrier. The format is similar to the Normal Burst, except without the flag bits
WITH BURST AND FRAME
- TDMA frame structure through the air begins to burst and developed until Hyperframe. Development occurs as follows:
- TDMA frame consists of 8 time slots. Each time slot carrying a single burst.
- 26 Traffic Channel TDMA frame containing a traffic channel multiframe; used to carry the TCH, SACCH and FACCH.
- 51 Control Channel TDMA frame contains a control channel multiframe; used to carry BCCH, TCCCH, SDCCH and SACCH.
· A superframe consists of 51 or 26 traffic channel multiframe control channel multiframe another.
· Hyperframe superframe consists of 2048
SIGNAL STRENGTH MEASUREMENT
Measurement of signal strength on idle mode and active mode
Idle mode
Idle mode occurs when the MS condition on but not connected (MS does not send a signal). When the MS in the conditions on, the MS is measuring all radio frequencies in the system and provides the signal strength for each frequency. MS to tuning into the best cell to receive messages or to request a connection. MS continues to monitor all the nearest cell, and also there is a better cell, the MS will to tuning into the cell.
MS is constantly updated measurement report containing the average signal strength to the nearest cell-cell, power and BER fractions of base stations serving. Signal strength from the serving BTS is measured each time by the MS receiving the assigned time slot.
Active mode
Active mode occurs when the MS communicates with the network. Both MS and the BTS serving (serving BTS) to measure the signal strength on the radio link. MS secra continuous reporting to the system of how strong the signal strength received from BTS. This measurement is used BSC to make the decision to target cell when the handover occurs.
MS also measures the quality (BER) on the downlink of the serving cell (serving cell). The measurement results are provided in MS and the average measurement calculated for all values provided for a period of 480 ms. Value calculations are sent to the BTS in the form of a report measurements every 480 ms. The average value of measurements for each carrier and then obtained and reported to the BSC. To ensure the measurement results related to the actual base stations, base station identity must be ascertained. The identity of the BTS is given in the BSIC, sent by SCH, time slot 0, carrier 0.
MS procedure when a new active:
- MS receives and measures the signal strength in the serving cell, time slot 2.
- MS transmits.
- MS measure signal strength to at least one of the nearest cell.
- MS read BSIC in SCH (time slot 0) to one of the nearest cell.
Six cell-cell closest to the average value of the highest signal strength and validation BSIC then reported to the BSC through the SACCH. When MS is not synchronized with the cell-cell closest, MS does not know when the time slot 0 in the BCCH-carrier will occur. Therefore, MS can be measured through an extended time period, at least 8 time slots, to ensure that the time slot 0 will occur during the time of measurement. All this is carried out during the IDLE frames.
Measurement Report
- Measurement reports consist of all data sent to the system by MS during the relationship lasts. The report was sent on SACCH every 480 ms. The data include:
- Signal strength on the serving cell.
- Mobile power is used.
- Timing Advance Value is used.
- Transmission Discontinues used or not
- The quality of the serving cell.
- Signal strength of cell-cell nearby.
- cell-cell numbers were reported nearby.
- Frequency BCCH to reports of cell-cell nearby.
- BSIC to report the nearest cell-cell.